PathoPic – image database / PathoPic ID 11301 - Sjögren Syndrom, kleine Mundspeicheldrüse, Entzündungsfokus
de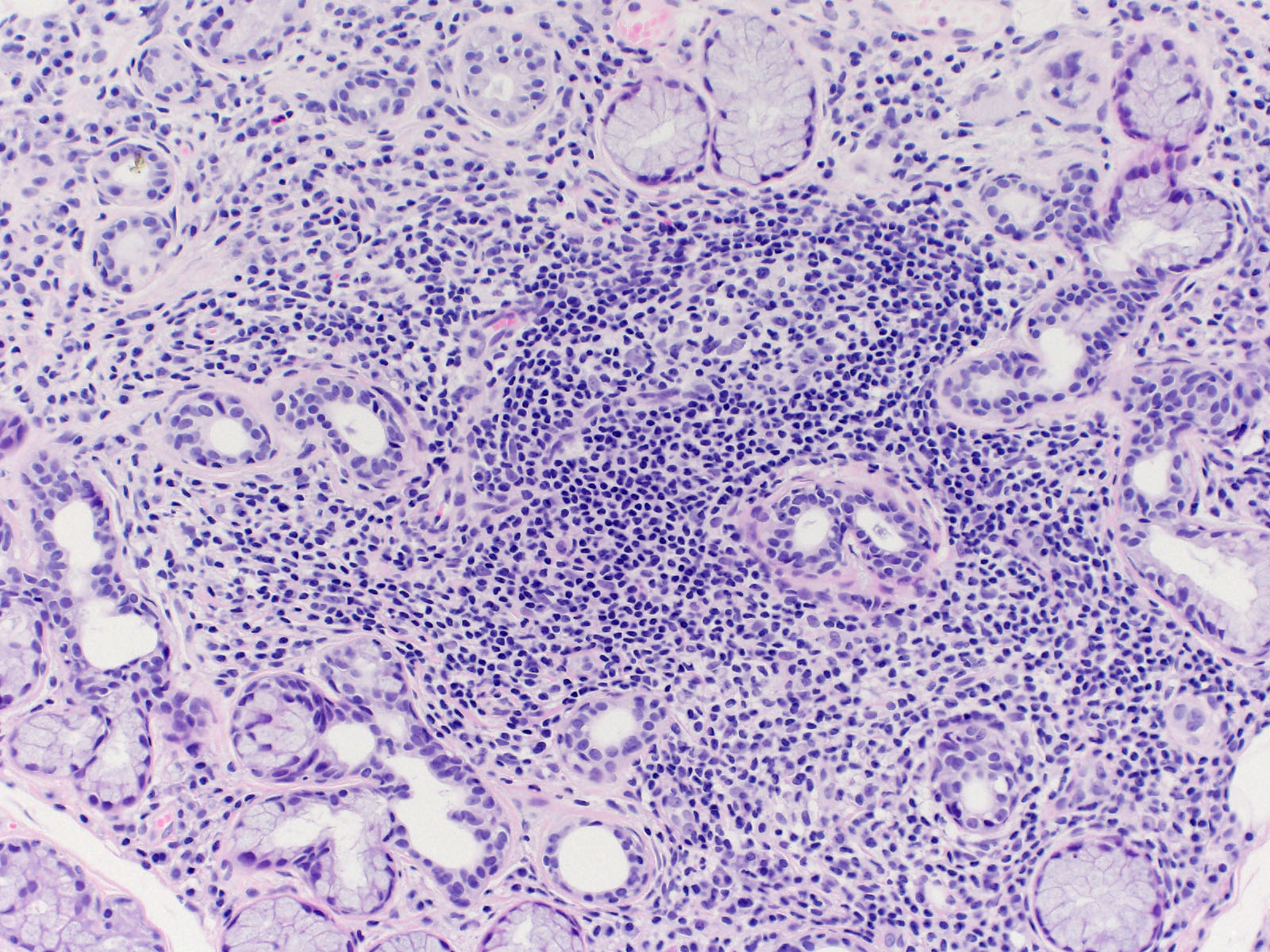
Diagnose
Sjögren Syndrom, kleine Mundspeicheldrüse, Entzündungsfokus
Diagnose Gruppe
Systemerkrankung/Immunpathologie
Topographie
Speicheldrüse
Topographie Gruppe
Kopf & Hals, Sinnesorgane
Beschreibung
Mehr als 50 mononukleäre Entzündungszellen in Nachbarschaft zu nicht atrophem Speicheldrüsenparenchym. Damit ist das histologische Kriterium für die Diagnose eines Sjögren Syndroms erfüllt. Zusätzlich hat sich im Zentrum des überwiegend lymphozytären Infiltrates ein heller imponierendes Keimzentrum ausgebildet.
Zusatzbefund
Insgesamt fanden sich 6 Entzündungsfoci mit mehr als 50 mononukleären Zellen in 4 Quadratmillimeter Speicheldrüsenparenchym. (Fokus Score 6, Grading nach Chisholm und Mason 4).
Klinik
68 jährige Patientin. Xerostomie. Serologie positiv auf Rheumafaktoren Anti SSA/RO (RO62/RO60). Anti SSA/RO52. Hinweis für M. Sjögren?
Kommentar
The prognostic relevance of analysis of salivary
gland infiltrates has recently been highlighted by
the observation that organisation of focal lymphocytic
infiltrates into germinal centres (GCs) is associated
with higher risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma
(NHL) and systemic disease. The number of foci in labial salivary glands has been shown to be positively
associated with GC formation.
Theander E, Vasaitis L, Baecklund E, et al. Lymphoid
organisation in labial salivary
gland biopsies is a possible predictor for the development of malignant lymphoma
in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 2011;70:1363–8.
Risselada AP, Looije MF, Kruize AA, et al. The role of ectopic germinal centers in
the immunopathology of Primary Sjögren’s syndrome: a systematic review. Semin
Arthritis Rheum 2012;42:368–76.
Bilder Typ
Histologie
Vergrösserung
200
Alter
68
Geschlecht
unbekannt
Datum
Ersteintrag: 05.03.2014
Update: 20.11.2019